Cloud computing can save you money is perhaps the most touted of the cloud’s many benefits and it’s easy to see why. It makes better economic sense to lease computer time rather than invest in costly hardware that will depreciate in value and require an ongoing cost to support and maintain. At least, in theory, and it ultimately comes down to how effectively you can manage your cloud.
During the process of cloud adoption, most businesses fail to set up a cloud cost-management framework, resulting in the high cost of services. According to one, organizations spend up to one-third of their cloud investment on services and resources that are less effective for their business. Fortunately, you don’t have to be one of them.
Here are 5 steps you can take that will help keep your expenses down, your revenue up, and your cloud costs under control.
Step 1. Retire Unused Cloud Resources & Instances
Keeping cloud costs low can be difficult for any organization but it can be especially difficult for those who are new to cloud computing.

For example, virtual machines on any cloud platform remain an expense even if they are idle or unused. On average, 15% of the cloud cost is associated with unattended and inactive services because such services are still leasing compute power. Businesses need to be careful about their cloud resource usage and consider cloud storage pricing accordingly. If you are not using particular resources or services – terminate it. These idle services or instances can be stopped manually through the cloud portals or by scheduling automated processes using scripts.
Automated scheduling is the most cost-effective method because it’s a one-time job and does not require ongoing human involvement to monitor all cloud services or instances. One can set up cloud instances to run during designated time windows (e.g. from Monday to Friday only) and can group worker nodes to stay alive, so they are not terminated after scheduled hours. In case you do not need the Virtual Machines and services, make a point to retire and eliminate the cost.
Step 2. Always Autoscale Cloud Resources To Save on Cloud Storage Cost
If you aren’t utilizing an auto-scaling mechanism then you are missing out on a key benefit of cloud computing. What auto-scaling does is, it buys capacity as needed; scaling up or down when required. The most common mistake in cloud engagements is buying more capacity than necessary. The more cost-effective method is to simply automatically resize your capacity as requirements dictate, without spending a lot on cloud storage pricing.
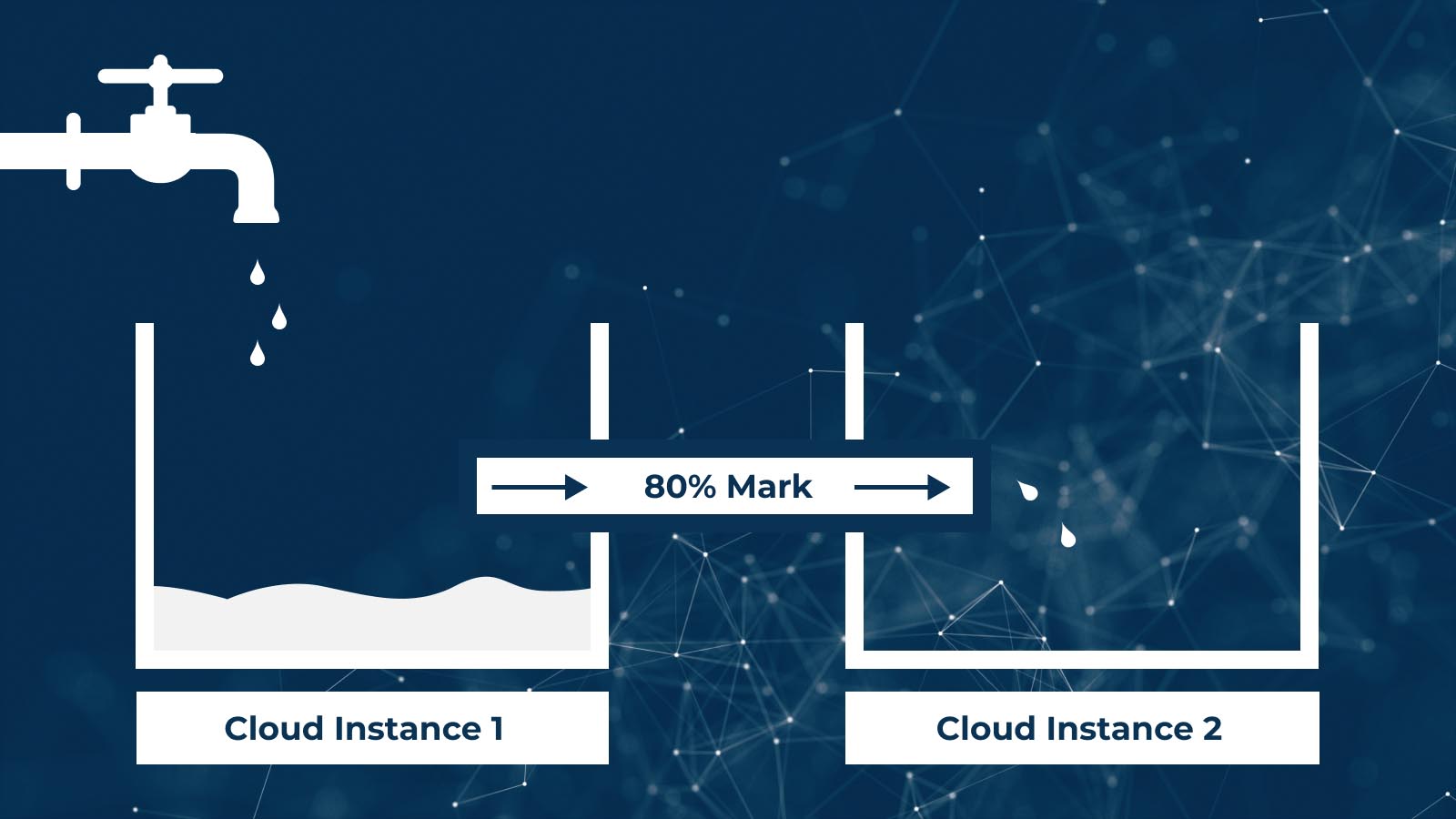
The figure above shows an implementation of an auto-scaling feature. As you can see, when a system reaches a threshold, another cloud instance is added to relieve the pressure. One use case is when a cloud instance serves all the user’s requests and fulfills their demand; however, the traffic only increases exponentially at peak hours. In such a case, a more appropriate approach will be to use an auto-scaling feature rather than using a more significant capacity cloud instance, which would be costly. This feature can automatically add up the same specification, additional instance, and balance the traffic load. When the user traffic falls to a reasonable threshold, the scaled instance will automatically shut down to save cost.
Step 3. Automation Techniques & Strategies
One can, and more importantly, should use cloud automation tools to setup and configure cloud computing services whenever needed. Automating tasks like the backup of virtual machines and storage units, source code deployments and unit tests execution, security, and compliance can minimize human involvement. This way, you can shift your focus from these “maintenance” tasks to higher-level design and strategic business processes. Dynamic asset provisioning can help setup strategies to avoid over-usage of resources.

There are some third-party tools such as Terraform that can even automate infrastructure level deployment. Its structure setup relies on source code and can be used to provision or modify on-demand. The code can be used to set up a single to multi-cloud configuration with just the help of scripts, significantly speeding up the provisioning process.
Step 4. Serverless Computing & Function as a Service
Serverless computing refers to using (and paying for) services for a particular time, and after that usage, the computing resources are returned to the cloud provider. This approach is also known as Function as a Service or FaaS. With FaaS, organizations only incur cloud costs when and if they are used. When the need arises to perform a business process or task, the service triggers the start of the instance and shuts down automatically after completion. It uses precise cloud resources to reduce the cost and maximize efficiency by avoiding unnecessary modules running all the time.

Step 5. Utilize Reserved & Spot Cloud Instances
Just like no two organizations are the same, the same could be said for their usage of the cloud. For example, taking a Reserved Instance Approach, or committing to a fixed amount of resources over a period of time, would be a cost-effective strategy if demand is steady, as it requires a long-term commitment. Taking such an approach for a year can yield savings of up to 40% while a three-year commitment could bet you 60% in savings.
Another cost-saving approach to consider is using Spot Cloud Instances. This is where unused instances from a service provider are purchased at steep discounts. Typically, a spot instance is 70% to 90% cheaper than the price of an equivalent-sized regular cloud instance. It is not without risk though, as that they can be shut down or closed at any point without notice. However, there are many different ways to mitigate that, and it’s impact like only using spot instances for low priority tasks or running stateless services that are not business-critical. An alternative approach to deal with this risk is to use auto-scaling, which can maintain a particular count of instances even if the spot instance is closed.
Take away
If managed and executed correctly, migrating to the cloud can undoubtedly save your business money. But it can also do much more than that. It can make your business more competitive, flexible, and able to adapt to rapid changes in customer demands. But to succeed, it requires planning, development, and investment to create the seamless experience you are after. Laying out a sequential strategy will help you build out your cloud capabilities and help you achieve a cost-effective and future-forward solution that provides value to both the user and your business.
The above was written in collaboration with Uzi Murad, Account Executive at mobileLIVE.